Home / Statistical Tools / Distribution Fit/Calc / Distribution Calculator / Binomial Distribution
Binomial Distribution¶
Probability Calculator¶
From Excel click...
QXL Stat Tools Tab > Distribution Fit/Calc > Distribution Calculator > Binomial
The Binomial distribution is a discrete probability distribution. It can be used to calculate the probabilities in a sequence of Bernoulli trials. A Bernoulli trial is a random experiment which results in success (with probability p) and failure (probability q = 1-p). The parameters of the Binomial distribution are n and p, where n is the number of trials and p is the probability of success on any trial.
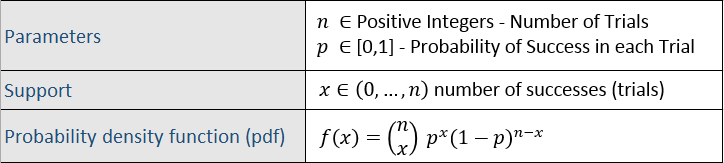
The Binomial distribution is often used to calculate the probabilities associated with a sample size of n draws from either an infinite population or drawn with replacement from a finite population. If the population is finite and the draws are made without replacement, then use the Hypergeometric distribution.
Example¶
A standard deck of playing cards (without Jokers) has 52 cards and four suits (diamonds, hearts, spades, and clubs). Suppose you decide to make 5 Bernoulli trials by drawing a card, recording the suit, andreplacingthe card. What is the probability of drawing five consecutive hearts?
Using the Binomial distribution...
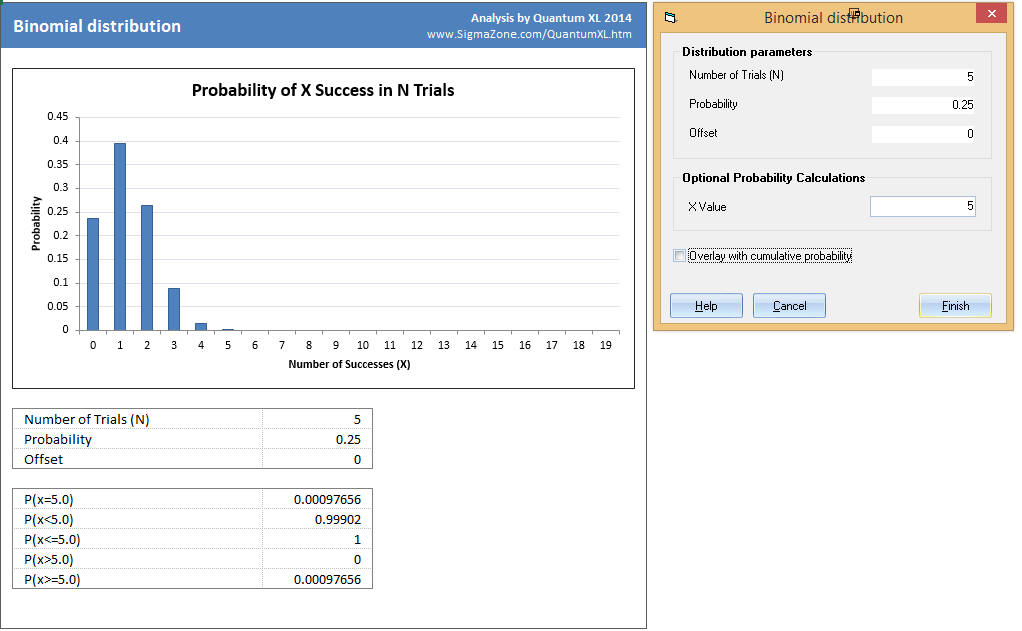
n = 5 (the number of trials) p = .25 (one fourth or .25 of the cards are hearts) x = 5 (five consecutive hearts)
The results from Quantum XL are below. The blue bars indicate the probability of having (x) successes. For example, the probability of having zero successes (drawing no hearts in five cards) is just under .25. The probability of drawing 1 heart is almost .4. The numerical values at the bottom of the analysis indicate the probability of five hearts, or P(x=5), is .00097656, which is not very likely.
However, if we were playing poker the Binomial distribution would not apply. In poker, the card is not replaced after every draw. Thus, the probability (p) changes with each draw. If you draw one card from a full deck, the probability of a heart is 13/52 = .25. If that card is a heart, then the probability of drawing a heart on the next turn is 12/51 = .235. To model this, you would need to use the Hypergeometric Distribution.