Home / DOE / Analyze / Nominal Logistic Regression
Nominal Logistic Regression¶
Nominal Logistic Regression is used by Quantum XL during Run Regression when the output is nominal. Nominal outputs are categorical but have more than two levels. If the output is categorical with two levels, then Binary Logistic Regression should be used. Example of nominal outputs would be Day of week (M/T/W/Th...), color (red, green, blue), etc.
Nominal logistic regression is actually a misnomer. Unlike Ordinary Least Squares Regression (OLS) the coefficients are an estimate of an iterative algorithm called Newton's Method.
Nominal Logistic Theory¶
Assuming the output (y) has r levels...
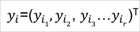
With index ni and parameter πi

Nominal logistic regression can relate πi to the covariates (inputs) through a set of r-1 baseline-category logits. Taking j* as the baseline category, the model is...
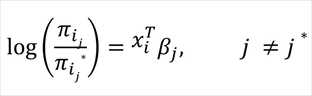
If xi (design matrix) has length p, then this model has (r-1) * p free parameters. These are arranged into a vector such that the last category is the baseline (j* = r), the coefficients are...
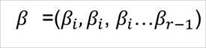
The kth element of βj can be interpreted as the increase in log-odds of falling into category j versus category j* (reference) resulting in a one-unit increase in the kth covariate while holding other covariates constant.
To calculate from πi (prediction) from βj (coefficients) the back-transformation for non-baseline categories is...
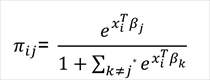
And the baseline-category probability is...
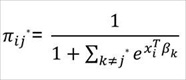
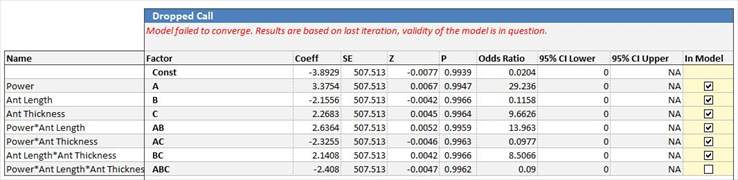
Newton's Algorithm, also known as Newton's iterations, are not guaranteed to converge. Quantum XL will warn you that a model failed to converge by displaying a warning in red at the top of the regression table.